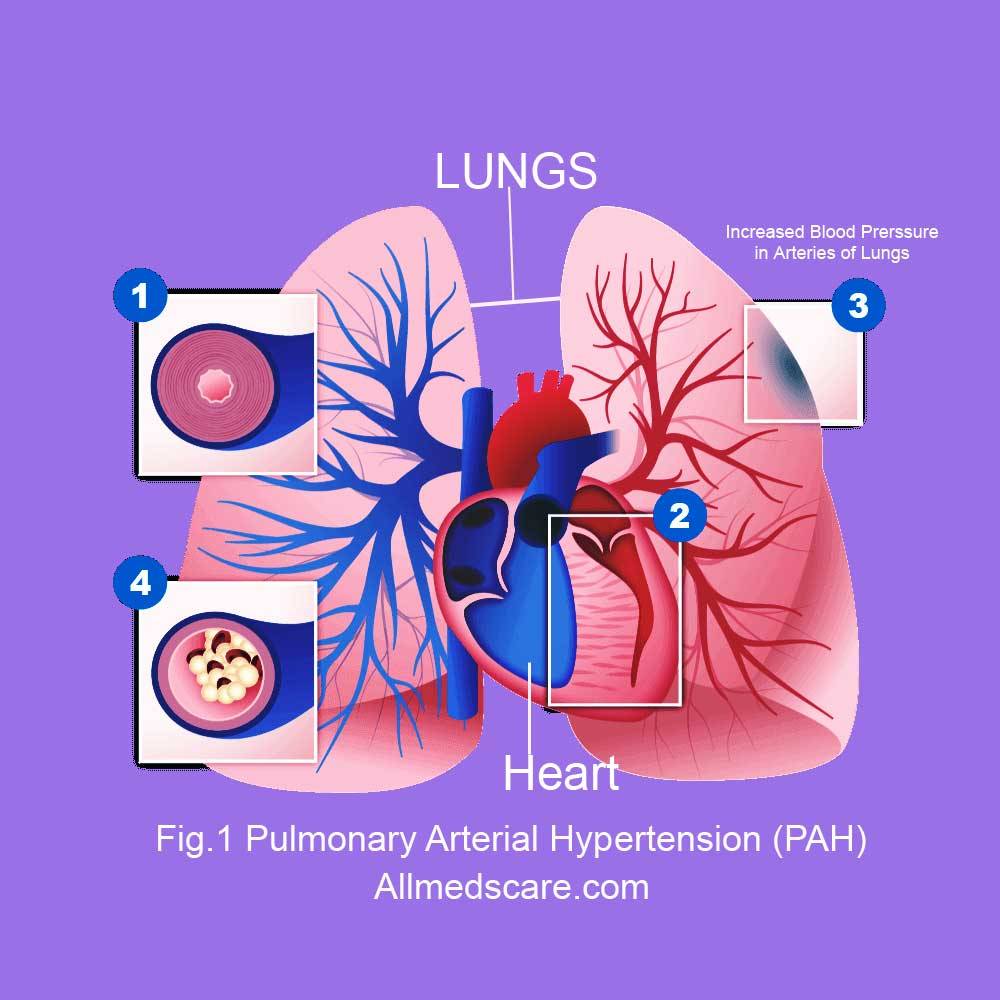
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH)
What is Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH)?
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) is a very serious health condition that damages the pulmonary arteries in the lungs. In this problem, the blood vessels that carry blood from the heart to the lungs cause high blood pressure. PAH occurs when these arteries become thickened, narrow, or stiff, which makes it difficult for the heart to pump required blood to the lungs, as a result, the heart has to work hard to circulate blood which leads to heart failure and other complications. In this article, we will discuss what is PAH, its causes, symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Symptoms of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
The symptoms of PAH can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Some of the common symptoms of PAH such as:
- Shortness of breath at the time of physical activity
- chest pain or pressure
- Fatigue
- Rapid heartbeat
- Swelling in the ankles or legs
- Bluish lips or skin
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms then you need to consult with your doctor for as better treatment.
Risk Factors or Causes of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
The proper cause of PAH is generally unknown, but there are so many risk factors that can increase the development of the condition. Some of the common risk factors or causes of PAH are as follows:
- Family History: In some cases, PAH can be genetics to run in the families.
- Medical Conditions: Medical conditions such as liver disease, connective tissue disease, or HIV are more likely to develop PAH.
- Diet Pills: Some diet pills such as Fen-Phen can lead to PAH.
- Congenital heart defects: some people are born with weakened heart or heart defects, which can lead to the development of PAH.
- Age: After the age of 60, PAH is a more common health condition.
- Gender: In women have more chances to develop PAh than men.
- Lifestyle Factors: Unhealthy lifestyle factors such as smoking, alcohol consumption, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle can lead to the risk of developing PAH.
- Idiopathic: The cause of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) is unknown in some cases.
Diagnosis of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Diagnosing PAH can be challenging due to the symptoms can be similar to those of other conditions such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). To diagnose PAH, your healthcare provider suggests several tests according to your physical exam, and medical history.
- Echocardiogram: This test creates images of the heart and lungs by using sound wave technology to show how well your heart is functioning and detect any abnormalities in the pulmonary arteries.
- Pulmonary function Tests: The test shows how well your lungs are working and what amount of air you breathe in and out.
- Chest X-ray: In that test conclude that the heart or lungs had any changes.
- CT Scan: This test provides detailed information about the lungs, as a result, the doctor can help to detect any abnormalities in the pulmonary arteries.
Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Right now, there is no cure for PAH, but several treatments are available to help manage the symptoms and decrease the progression of the condition. Here is the list of common treatment options for PAH.
- Medications: Sildenafil Citrate rich medications are often used to treat PAH. It works on your blood vessels to relax them and improve blood flow and decreases the blood pressure in your lungs which makes it easier for the heart to pump blood to the rest of your body.
- Oxygen Therapy: Supplemental oxygen can help improve oxygen levels in the blood and reduce the workload on the heart.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: These programs include exercise and breathing techniques that help work lung function in a proper way and reduce symptoms of PAH.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery is required to replace or repair damaged heart valves, transplant a new lung or heart lung, or remove blood clots.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adapting healthy lifestyle choices, like maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and avoiding high altitudes helps manage symptoms of PAH.






