Chronic Kidney Disease
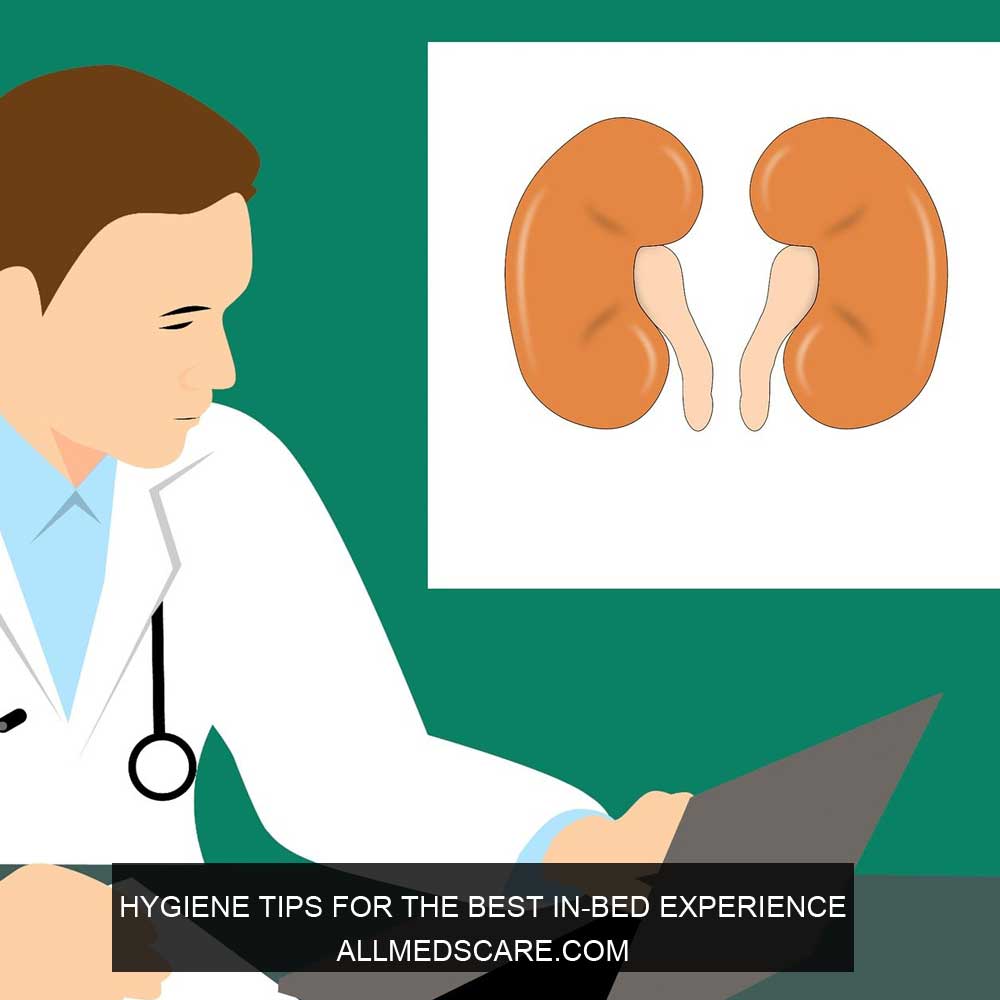
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a long-term health issue that affects the functioning of the kidneys. When the kidneys are damaged and unable to filter blood properly, as a result, the build up of waste and excess fluid in the body. CKD affects around 13 million people in the United States only and leads to serious health complications such as the risk of cardiovascular disease. Chronic Kidney Disease is a silent killer and progresses slowly over time and goes unnoticed until the later stages. Some common symptoms of CKD include nausea, swelling in the extremities, loss of appetite, fatigue, and difficulty urinating. If anyone leaves it untreated it can increase End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD), in that situation dialysis can be required for survival. However, people can live a fulfilled life if they detect it early and are managed properly to help slow down CKD progression and avoid ESRD.
Understanding Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Chronic Kidney disease is a health issue that develops over several months or years. CKD is characterized by the loss of kidney function that leads to kidney failure. The kidneys play a vital role in our body by filtering waste and excess fluid from the blood regulating blood pressure and producing hormones important for bones and red blood cell production. When the kidneys are not functioning well, waste and fluid can build up in the body which can cause a range of symptoms and complications.
Symptoms of Chronic Kidney Disease
Lots of people experience no symptoms at all in the early stage of CKD. As the disease grows, people can experience symptoms like fatigue, loss of appetite, weakness, vomiting, swelling in the feet and ankles, difficulty sleeping, and nausea. Some of the other symptoms such as itching, muscle cramp, dry skin, and changes in urine output. In extreme cases, CKD may be a risk factor for high blood pressure and anemia.
Causes of Chronic Kidney Disease
There are so many factors that can contribute to developing CKD. Some most common and typical causes of CKD are high blood pressure, diabetes, and inflammation of the kidneys. Polycystic kidney disease, kidney infection, and kidney stones are the other causes that can damage kidney function. Lifestyle factors such as a diet high in salt, obesity, and smoking may lead to the risk of developing CKD. Genetic defects are one of the causes of CKD. Some inherited conditions such as Ig A nephropathy, Alport syndrome, and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) may produce CKD.
Certain medications can also lead to CKD. Drugs such as ibuprofen are one of the causing factors of kidney damage when consume over a long period as they affect blood flow within the organ. some antibiotics that are used to treat urinary tract infections may also lead to the risk of CKD. If any potential risks are associated with taking medications then they must consult with their healthcare provider.
Diagnosing Chronic Kidney Disease
Screening and diagnostic tests are the first step in diagnosing CKD. A general blood test can be used to measure urea nitrogen, creatinine, electrolytes, and other factors in the kidney’s waste products. if any of the above measurements are abnormal it can show a problem with kidney function. Urine tests can also be one of the best diagnostic test help to detect infection within the urinary tract.
Physical exams are the key component tests diagnosing Chronic Kidney Disease.
In the physical exams, doctors generally check eyes or limbs if they swell it could be a signal of fluid retention because of impaired kidneys. They also check an enlarged abdomen that may be an indication of cysts on the organ’s surface. In addition, They can also take note of any changes in the skin with certain types of CKD such as dark patches known as uremic frost caused by toxins building in the body when the kidney is not functioning properly.
Finally, some tests such as X-rays or CT scans may be required after the initial screening and physical exams are done. These tests are very useful to physicians to come to a closer look at what is going on inside your kidneys. So, according to that, they can better understand and take a better treatment for CKD.
Managing Chronic Kidney Disease
Managing Chronic Kidney Disease needs a thorough approach that added exercise, diet, and medications. Changing a diet plan is a very effective step in managing CKD. Adding vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and fruits may help to reduce the strain on the kidneys. Moreover, reducing salt intake is advised as it helps prevent fluid retention in the body, which can make CKD symptoms worse. Finally, it has been demonstrated that restricting caffeine intake is advantageous for those with renal disease because this stimulant can raise blood pressure levels, which may already be high owing to damaged kidneys.
Another essential element for CKD management is consistent exercise. Exercise not only increases energy levels but also enhances blood flow throughout the body, reducing the strain on the kidneys caused by the filtration of waste from your bloodstream. While managing chronic diseases, low-impact exercises like walking or swimming are frequently advised since they put less stress on your heart and lungs while still offering plenty of opportunities to gradually improve your cardiovascular fitness.