Tuberculosis- Full Authentic Information, One must know!
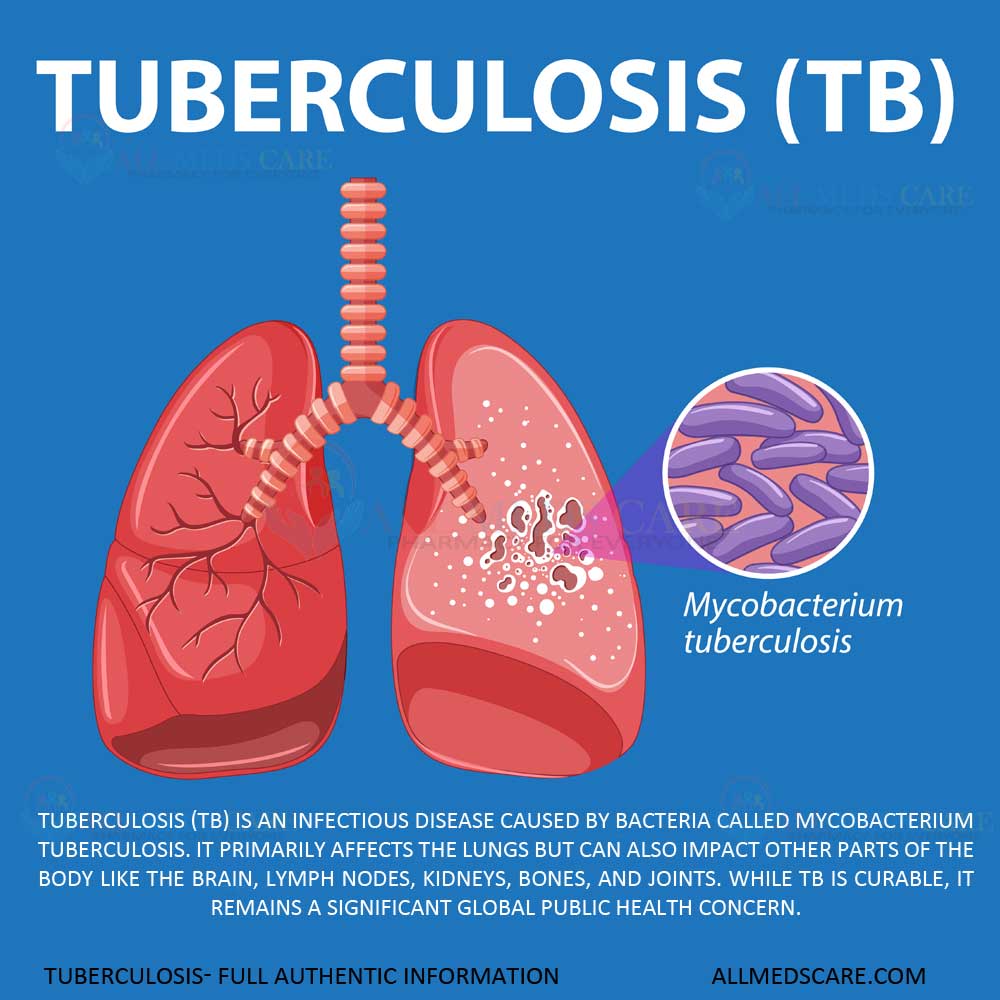
Tuberculosis (TB) disease is not a dangerous disease until people avoid taking treatment at the right time. This disease is a preventable and safely curable infectious disease caused by bacteria, mainly affecting the organ lungs.
This bacteria mainly spreads through the air when people with lung TB cough, sneeze, or spit, releasing infectious droplets. Most of the people infected with TB bacteria disease develop a latent infection. In this type of infection, bacteria are present but not active.
Tuberculosis Death Rate
According to the health report, In 2023, 1.25 million people died from tuberculosis worldwide including 161,000 people with HIV. The Case Fatality Rate (CFR), which is the proportion of people who have TB and lost their life from the disease, was 11.5%. This means that, on average, about 1 in 9 people diagnosed with TB lost their life from the disease.
Specific Regions: High TB burden countries had a significantly higher mortality rate (25 per 100,000 population) compared to the global average.
Types of Tuberculosis
-
Pulmonary: This type of TB is the most common form and affects the organ lungs health, with symptoms like persistent cough, fever, and sudden or gradual weight loss.
-
Extrapulmonary: This type of TB can affect various organs and tissues, such as lymph nodes, bones, joints, brain, kidneys, and even the skin. This type of TB will reveal symptoms depending on the affected area.
-
Latent: This type of TB is called a “silent infection” because this type of bacteria in a person’s body does not feel sick and cannot spread the disease.
-
Active: This type of TB disease occurs when the latent infection progresses and the Tuberculosis bacteria start increasing quickly, causing symptoms and making the person contagious.
-
Miliary: This type of TB is a rare type of TB, but this is a serious form of Tuberculosis where the bacteria spreads through the bloodstream to multiple organs, causing a wide range of symptoms.
Tuberculosis Disease
Symptoms of this disease depend on where in the body the germs are growing. The germs commonly grow in the respiratory organ lungs (pulmonary Tuberculosis).
Tuberculosis disease in the lungs may cause symptoms such as:
-
A bad cough that lasts 3 weeks or longer
-
Pain in the chest
-
Coughing up blood or phlegm from deep inside the lungs
Other symptoms of Tuberculosis disease are:
-
Weakness or fatigue
-
Weight loss
-
No appetite
-
Chills
-
Fever, and
-
Sweating at night.
Symptoms of Tuberculosis disease in other parts of the body depend on the area affected:
-
Disease of the lymph nodes : causes a firm red or purple swelling under the skin.
-
Disease of the kidney : causes blood in the urine.
-
Disease of the brain : causes severe headache or confusion.
-
Disease of the spine : causes severe back pain.
Reason for Tuberculosis
Bacteria:
The disease is mainly caused by the bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. These bacteria are intracellular aerobic, meaning they require oxygen to live and grow more numbers. These bacteria have a unique cell wall that covers them from the body’s defenses.
These bacteria first infect the lungs then it slowly spreads to other organs via the bloodstream or lymphatic system.
How this Bacteria Spreads?
People should know about this bacteria and how it spreads from one person to another person. Tuberculosis bacteria is spread through the air when people with active cough, sneeze, or speak. Little droplets loaded with Tuberculosis bacteria are released into the air and can be inhaled by others.
People who keep close contact with someone who has active Tuberculosis is a major risk factor, and one more thing, it is not spread by touching or sharing food or dishes. So, don’t panic about patients, but always keep some distance.
Who get this Disease very quickly?
- Poor Immune System: People having lack or poor immune systems, such as those with diseases like HIV/AIDS, doing chemotherapy, diabetes, or certain medications, are at higher risk of developing this disease.
- Close Contact: People who are spending a lot of time with someone who has active tuberculosis increases the risk of infection.
- Smoking tobacco habits: Smoking tobacco habits and exposure to second-hand smoke increase the risk. One must give up smoking. There are plenty of medications available to help you that.
- Other Reasons: Other reasons such as poverty, malnutrition, poor housing, and limited access to healthcare also increase the risk of tuberculosis.
Tuberculosis Treatment
The treatment mainly involves taking a combination of antibiotics for a prolonged period from 4 to 9 months to completely vanish the bacteria and avoid the development of drug resistance. These antibiotics such as isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol. This treatment also includes absorbing the TB patients for side effects and ensuring complete adherence to the prescribed regimen.
Prevention measures for Tuberculosis diseases
Taking a prevention method is the best way to avoid TB disease in the early stage. People should know about these prevention methods.
-
Vaccination
-
Early Diagnosis and Treatment
-
Preventing Spread of Infection
-
Good Ventilation
-
Good Hygiene
-
Avoiding Close Contact
-
Environmental Controls
TB patients should follow doctor advice which surely gives good results and avoid this disease completely.