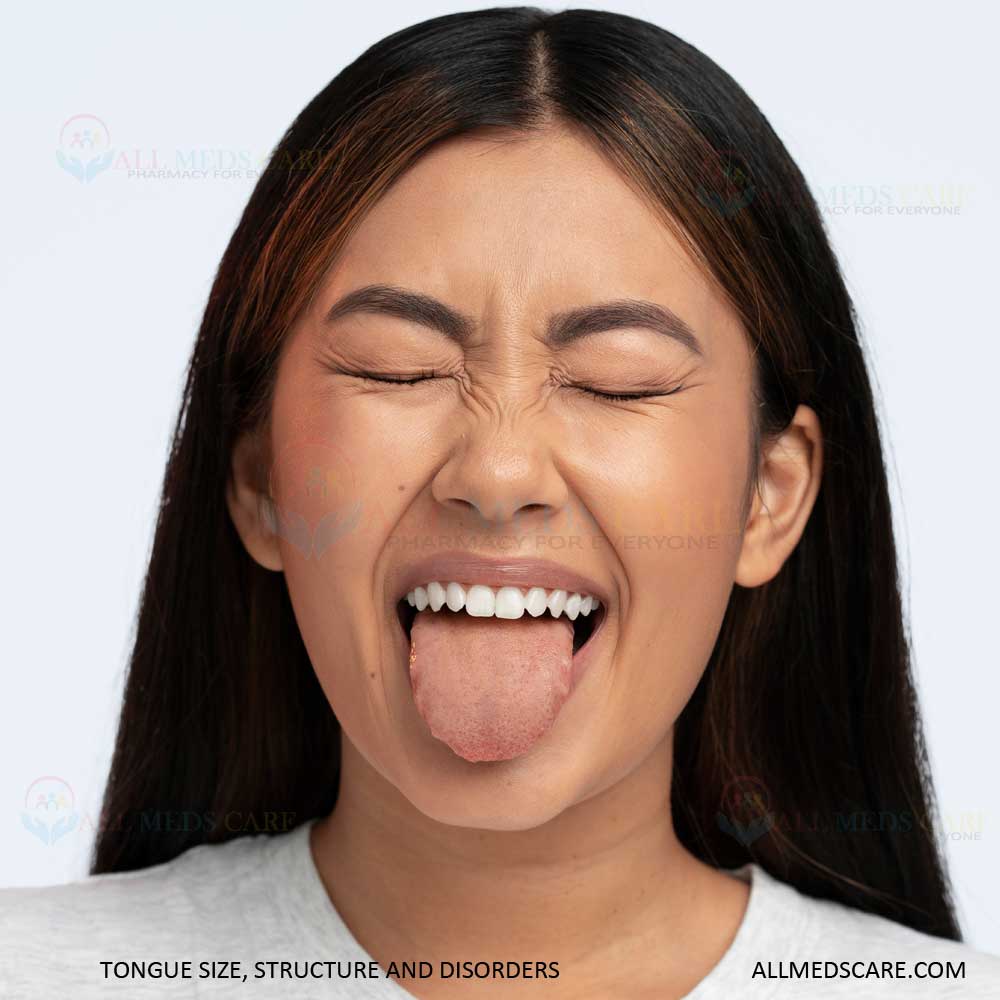
Tongue size, structure and disorders
Human body has different organs and each organ does its own function to keep the body healthy and active. Tongue is an important organ to eat the food, it is playing a marvellous role while eating food. Human beings taste different food items with the help of this organ. Tongue is not only important for eating food and tasting the food, but also humans need to speak very well. In this article we see in depth about the tongue structure, function and many more.
What is Tongue?
Tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth that helps with chewing, speaking and breathing. It also supports producing more mucous and saliva which keeps the mouth moist. This organ is placed inside the mouth. The organ moves with the help of a hyoid bone located in the middle of the neck.
Tongue Size
The average human tongue is about 7.6 cm length and 6.4 cm width. But the human tongue size is different based on few things that can affect it such as
- Sex: Commonly men have longer size than women, measuring 8.5 cm compared to 7.9 cm.
- Growth: The tongue increases size, length, breadth, and thickness between birth and adulthood.
- BMI : Larger size is based on higher BMI.
Tongue Structure
Tongue is made up of muscles and it is covered by mucosa. It has commonly six main parts, they are:-
- Root
- Body
- Apex
- Dorsum
- Inferior surface
- Lingual frenulum
The frenulum linked the tongue to the floor of the mouth, this will helps the tip to move freely.
Types of papillae
Tongue is also covered with various types of papillae (bumps) and taste buds. Commonly tongue having four different types of taste buds.
- Filiform – It is located on the front two-thirds of the this organ. It looks thread-like in appearance. Commonly other types of papillae have taste buds, but filiform papillae don’t contain any taste buds.
- Fungiform – This papillae looks like mushroom shape. It is located mostly on the sides and tip of this organ. This fungiform papillae contains approximately 1,600 taste buds.
- Circumvallate – The circumvallate papillae is placed at the back and it looks like small bumps. This papillae looks larger than the other types of papillae, and it contains approximately 250 taste buds.
- Foliate – The foliate is located on each side of the back portion, and this papillae look like rough folds of tissue. Human beings have 20 foliate papillae, which contain several hundred taste buds in the tongue.
How do taste buds work?
Taste buds are clusters of nerve cells that pass sensory messages to the brain. Commonly five basic tastes that encourage taste buds such as
- Sweet
- Salty
- Bitter
- Sour
- Umami
Many of them believe misinformation that different places of the tongue taste different things. But the fact is, all taste buds have the ability to find all five flavors.
Conditions and Disorders
- Changes in taste: When a person’s tongue has a change in taste, that condition is called Dysgeusia and a total loss of taste is called ageusia. Both these conditions happened due to infections, nerve problems, certain medications or damage to taste buds.
- Numbness
- Numbness can be a signs of many different conditions, such as:
- An allergic reaction to consuming certain foods or tasting chemicals.
- Autoimmune diseases like lupus, scleroderma or multiple sclerosis (MS).
- Raynaud’s phenomenon, a condition in which small blood vessels contract.
- Nerve damage due to dental work in the mouth or apply tongue piercing.
- Poor level of vitamins or minerals, such as calcium, iron, zinc and phosphorus.
- Certain duration of numbness or tingling is a sign of stroke. If numbness is continuing for a long duration, this will cause facial droop, difficulty speaking, confusion, dizziness, loss of vision or severe headache. When a person has these types of signs, seeking immediate health care help is good to avoid several health effects in the future.
- Numbness can be a signs of many different conditions, such as:
- Sore, bumpy: Irritations, minor infections are the most common reason for the soreness. Smoking habits for long duration is also the reason for this type of discomfort. In a few cases, a soreness can be a sign of oral cancer.
- Burning: If the mouthfeels burnt or scalded, this condition is called burning mouth syndrome. This burnt condition isn’t causing any harmful effects, but it can be causing too much discomfort. Anyone can face this health issue, but most commonly women face it during postmenopausal period.
- Macroglossia: The average size is 7 cm long and 6 cm wide. An enlarged condition is called Macroglossia. This condition arises due to trauma, inflammatory conditions or certain health issues like primary amyloidosis.
- Atrophic glossitis: When this organ loses its bumpy texture and appears completely smooth, this condition is called Bald tongue or Atrophic glossitis. Baldness is a sign of anemia or a vitamin B deficiency.
- Cold sores: Mostly cold sores formed on lips, they can also appear on the organ. This Cold sores mainly arise due to highly contagious herpes simplex virus.
A healthy tongue is always in pink color. The pink color may be dark due to shades of light. If the color is changed from pink to some other color, it will indicate warning signs of certain health issues. People should take the right action with the help of doctor advice. What do different colors signify?
- White– It indicates thrush, lichen planus, leukoplakia or other conditions.
- Red or purple– It indicates harmless conditions like geographic tongue. It is also a warning sign for vitamin deficiencies, scarlet fever or Kawasaki disease.
- Black– It indicates black hairy tongue.
- Yellow– It indicates bacterial overgrowth, and warning signs of psoriasis or, rarely, jaundice.