Psychotic Disorders- Types and Treatment Options
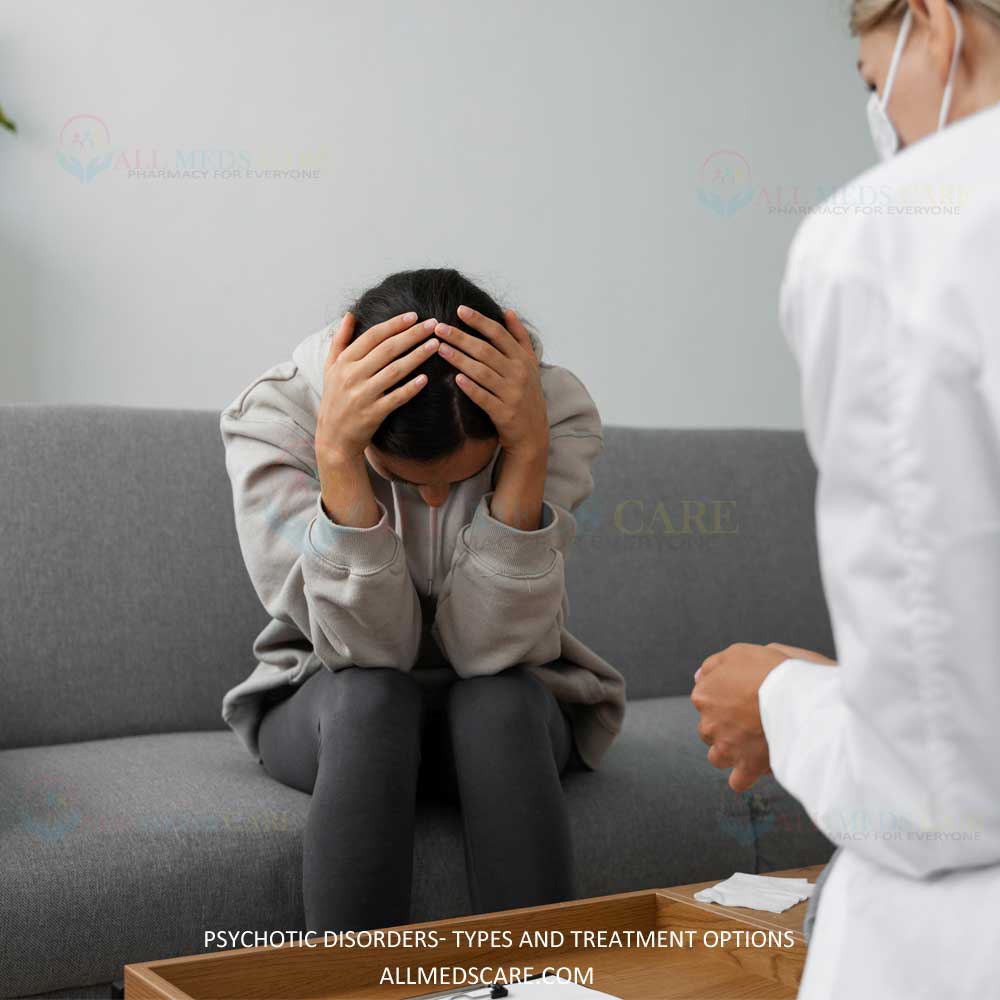
Psychotic disorders form a complex and commonly misunderstood class of mental disorders that have difficult implications in a person’s ability to analyze reality. Such disorders can ruin a life, but at the same time, can be easily treated with the help of such care, support, and education. In this extensive guide, the different types of psychotic disorders, probable symptoms, methods of treatment, need for early intervention, and how patients and their relatives can cope with the problem will be discussed.
What Are Psychotic Disorders? An Overview
Psychotic disorders are a collection of severe mental disorders that involve the detachment of the person from reality. This dissociation with reality is called psychosis, which hampers how one thinks, feels and behaves. It may be temporary or permanent, and may be present as part of other mental or physical well-being.
Definition of Psychotic Disorders
A psychotic disorder refers to any mental health condition in which psychosis is a prominent feature. Psychosis can cause:
- Delusions: Beliefs that a person holds strongly, even if there is proof, they are not true.
- Hallucinations: Experiencing things such as voices or visions that don’t exist.
- Disorganized thinking: Trouble organizing thoughts or speech.
- Abnormal behaviors: Erratic or unpredictable actions.
Understanding Psychosis
Psychosis is not a permanent state and can appear and disappear because of mental health, drugs, some illnesses, or a lot of stress. If a person goes through psychosis, they can lose track of reality and have strong emotions and feelings of withdrawal.
Psychosis is often found with these mental health problems.
Psychotic symptoms can be present in:
- Schizophrenia
- Bipolar disorder
- Severe depression (with psychotic features)
- Postpartum disorders
- Substance use disorders
- Neurological conditions (e.g., dementia, brain tumours)
Knowing the root cause is important when giving the best treatment and support.
Types of Psychotic Disorders: The Spectrum to Explore
Psychotic disorders manifest in several forms bearing their peculiarity. Recognizing the type of psychotic disorder is paramount in laying down the treatment plan.
- Schizophrenia
Chronic schizophrenia is characterized by persistent psychosis, such as hallucinations, delusions, and cognitive problems. Symptoms are typically divided into:
-
- Positive symptoms (additional experience, such as hallucinations)
- Negative symptoms (loss of function, for example, emotional expression);
- Cognitive symptoms (memory and attention problems)
- Schizoaffective Disorders
This condition is the amalgamation of schizophrenia’s symptoms and the mood disorder elements (depression or bipolar disorder). They manifest psychotic episodes while they have long-term disturbances of mood.
- Delusional Disorders
Individuals with delusional disorder exhibit strong false beliefs (delusions), lacking other noteworthy psychoactive symptoms. These entail paranoia, being grandiose, or having strange scenarios.
- Brief Psychotic Disorder
A brief episode of psychosis, lasting less than a month, that is usually precipitated by extreme stress or trauma. Proper treatment sees recovery of the disorder for most people within a short time.
- Substance-Induced Psychotic Disorder
Psychotic symptoms due to drug use (e.g. methamphetamines, LSD, alcohol withdrawal). Symptoms normally disappear when the substance is out of the system.
- Postpartum Psychosis
A rare pathology after delivery, characterized by hallucination, delusion, and extreme mood change. It is in an emergency state because of risks to mother and child.
Common Symptoms to Identify in Psychotic Disorders
Early diagnosis of psychosis can have a tremendous impact on the outcome of the treatment. Symptoms can look different between disorders, but usually include:
Core Psychotic Symptoms
- Delusions: Holding on to beliefs that don’t make sense or cannot be supported.
- Hallucinations: Experiencing things like voices, sights, or sensations that aren’t real.
- Disorganized speech or behavior: Incoherent thoughts or unpredictable actions.
- Negative symptoms: Low motivation, spending time alone, expressing less emotion, or neglecting personal hygiene.
Cognitive and Emotional Symptoms
- Memory problems
- Poor concentration
- Mood changes such as depression and mania
- Paranoia or extreme suspicion of others
Usually, symptoms appear slowly, and the affected person may feel unaware of their condition. Thus, putting the onus on friends and family to take action for rescue during the early stages.
Treatment Options for Psychotic Disorders: A Multi-Faceted Approach
Treatment is usually a variety of therapies that are personalized to the individual.
- Antipsychotic Medications
Antipsychotics are the cornerstone of treatment, helping to alleviate or eliminate the patient’s psychotic symptoms. These medications modify neurotransmitter function in the brain, particularly dopamine. These include:
-
- Risperidone
- Olanzapine
- Aripiprazole
- Clozapine-for instances of treatment resistance
The side effects are varied and include weight gain, fatigue, movement disorders, and others. Usually, medication is supervised closely to adjust dosage and side effects.
- Psychotherapy for Psychosis
Psychotherapy opens a safe place for the person to talk about thoughts and feelings, to learn about the illness, manage stress, and develop coping skills. Methods of psychotherapy include:
-
- Individual counselling
- Family therapy
- Group therapy
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT teaches patients how to recognize distorted thinking and integrate delusional beliefs. It reduces the effects of hallucinations and improves people’s functioning. CBT is best used in combination with medication.
- Support Groups for Mental Illness
They bring the essence of socialization and belonging. Sharing experiences with people facing similar kinds of struggles helps parties feel less isolated, while also providing some practical tips on coping. Support groups are commonly available both in-person and online.
The Role of Early Intervention in Optimizing the Outcomes for Psychotic Disorders
Utilizing the first episodes of a psychotic disorders is one of the most helpful approaches to achieving positive long-term results.
Early Signs of Psychosis
Some signs and symptoms during the prodromal phase of psychosis may be:
-
- Withdrawing socially
- Having unusual thoughts or suspicions
- Decrease in school/work performance
- Changes in sleep or appetite
- Problems with thinking clearly
Recognizing these signs can lead to faster diagnosis and better recovery outcomes.
Importance of Diagnosis and Treatment Timing
Other considerations of outcomes associated with delayed diagnosis and treatment, or Duration of Untreated Psychosis (DUP), include:
-
- Increased chances of relapse
- Less chance for a proper treatment response
- Higher chances of suicide or self-harm
Within this, early diagnosis and treatment programs, mostly aimed at first-episode psychosis, tremendously reduce the risk.
Prevention Through Early Intervention
These early intervention programs attempt to provide multidisciplinary care: psychiatric assessment, therapy, case management, and support in education or employment. The majority of the services were designed for young individuals with their first psychotic episode, with strong evidence for good long-term outcomes.
Coping Strategies and Support Systems for Psychotic Disorders and Their Families
The need to cure a psychotic disorders does not take place in isolation. It requires long-term care, changes in lifestyle and input from family support systems.
Coping Mechanisms for the Psychotic Patients
- Medication adherence: Always adhere to the course of treatment.
- Stress management: Rely on practices, such as yoga, meditation, or exercise.
- Healthy routines: Keep a normal sleep, eating pattern, and activity.
- Avoiding triggers: Recognize stressors or any environment that may elicit the symptoms and control them.
Family Support Affecting Mental Health Recovery
Family support is crucial for treatment. Families may:
- Provide emotional support and encouragement;
- Learn about the disorder to be able to provide the best care;
- Encourage treatment adherence; and
- Watch for any signs of relapse.
Family therapy can also help minimize conflict and strengthen communication.
Community Resources for Families who have Mental Illness – Affected Families
Several organizations and programs can help families:
- NAMI (National Alliance on Mental Illness): Provides free education, advocacy, and support groups.
- Mental Health First Aid: Trains the public in recognizing and responding to mental health crises.
- Local mental health clinics: Offer outpatient services, support groups and case management.
A strong support network can minimize caregiver burnout and empower families to take the best care