Living With Peripheral Neuropathy: What You Should Know
Peripheral neuropathy is one of the common problems in the nervous system, which affects many people around the world. Although it shows a lot, it is often uncontrolled or not understood until the signs actually mess up with everyday life. Peripheral neuropathy can manifest in many ways, such as tingling and numbness of the hands and feet, intense nerve pains, and muscle weakness, among many other variations depending on the nerve involved.
This post will help you find out what peripheral neuropathy is, including its signs, ways to find it and the treatment options, with changes in useful lifestyle and home remedies to improve your life.
What is peripheral neuropathy?
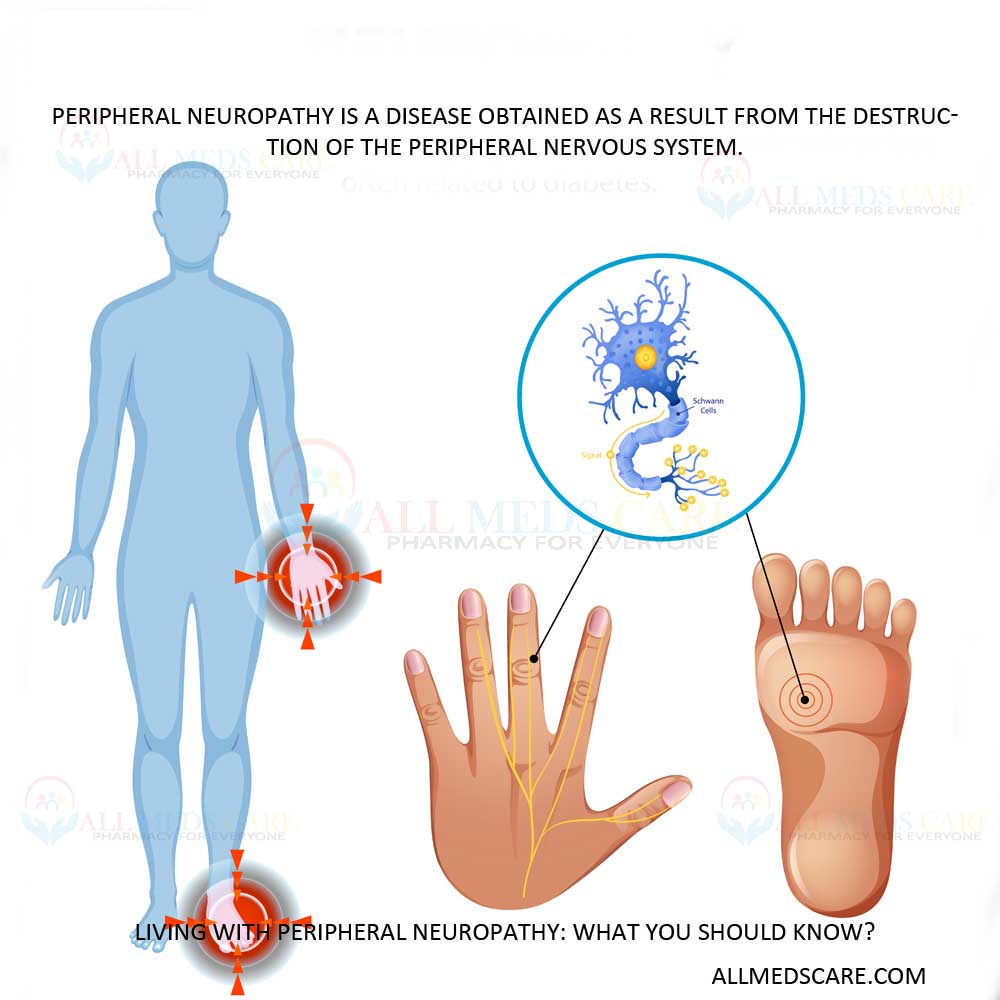
Peripheral neuropathy is a disease obtained as a result from the destruction of the peripheral nervous system, the complex networks of nerves located outside the brain and spine. These veins further take out these signs of the central nervous system, which are used to monitor movement, sensation and automatic body processes such as digestion, circulation and breathing.
By damaging these nerves, the wave of communication between the body and the brain is prevented, leading to a much wider range of symptoms.
Neuropathy definition
Neuropathy is a generalized term that refers to nerve damage that affects the transmission and reception of signals. Symptoms may be sensory, motor or autonomous, depending on the veins involved in trauma.
Types of Neuropathy
- Sensory Neuropathy – Affects the sensation. Patients are developed by burning, tingling or numbness in extremities.
- Motor Neuropathy – Affects the muscles and causes weakness, cramps, twitches or lack of coordination.
- Autonomous Neuropathy – Neurons that regulate automated body functions are damaged, causing digestive problems, irregular heartbeat and blood pressure.
- Combination Neuropathy (Polyneuropathy) – In most instances, multiple types of nerves are affected simultaneously.
The disorder of the nervous system may have different manifestations; thus, neuropathy may be hard to diagnose without medical examination.
Common Symptoms of Peripheral Neuropathy You Shouldn’t Ignore
Neuropathy symptoms can be acquired slowly and deteriorate with time. Identifying early warning signs is essential for preventing difficulties.
- Pain or numbness in feet, legs, fingers – tingling (pins and needles).
- Hands and feet can experience numbness, and the circumstance may additionally unfold to arms and legs.
- Sharp, stabbing, or painful, sharp, and normally nocturnal pains.
- Touch/temperature sensitivity.
- Weakness of muscular tissues, muscle cramps or twitching.
- Problems of balance and coordination leading to falls.
- Digestive problems along with constipation, diarrhea, or bloating (autonomic nerve involvement)
- Dizziness or fainting due to surprising blood pressure drops
These neuropathy signs and symptoms are uncomfortable, but they can also result in heightened dangers of injury (along with noted foot wounds in diabetic patients). Treatment of neuropathy can be carried out via effective pain control that consists of clinical therapies as well as lifestyle changes.
The Different Causes of Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is not just one condition; it usually happens because of another health issue. It is essential to find the reason to treat.
- Diabetes-Related Neuropathy
Diabetes mellitus is the most frequent cause of peripheral neuropathy. High blood sugar impairs nerve cells and decreases blood flow, causing progressive nerve damage.
- Hereditary Factors
Genetic problems like Charcot-Marie-Tooth disorder assault the peripheral nerve and may be hereditary.
- Autoimmune Diseases
Disorders like lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and Guillain-Barré syndrome mistakenly attack nerve tissues.
- Neuropathy Caused by Infections
It is known that nerve inflammation is provoked by viruses (shingles, HIV, hepatitis C) and bacteria (Lyme disease, leprosy).
- Nutritional Deficiencies
Lack of vitamins, especially Vitamin B12 deficiency, folate and vitamin E, can lead to permanent nerve damage if not treated.
- Alcoholism and Toxins
With chronic alcohol use, malnutrition and direct toxic nerve damage occur. Risk of neuropathy is also elevated by exposure to heavy metals and some chemicals.
- Medications
There are no fewer than some chemotherapy agents, antibiotics, and antivirals that cause neuropathic side effects.
- Physical Trauma or Surgery
Neuropathy can be caused by accidents, repetitive stress injuries or compressed nerves (as with carpal tunnel syndrome).
Diagnosis: What is the Diagnosis of Peripheral Neuropathy among the Healthcare Professionals?
Neuropathy diagnosis is a complex task that needs a thorough examination by a neurologist. The process normally involves:
- Neurologist Examination – Reflex testing, muscle strength assessment, and sensory evaluations.
- Nerve Conduction Studies – Test conduction speed of electrical signals along the nerves.
- Electromyography (EMG) – Monitors the activity of the muscle to show nerve and muscle damage.
- Blood Tests to Diagnose Neuropathy – Help diagnose diabetes, vitamin deficiencies, thyroid problems or infection.
- Imaging Tests (MRI or CT scans) – Diagnose tumour, herniated discs or nerve compression.
- Nerve Biopsy (rare cases) – A small part of a nerve tissue that has been diagnosed with a microscope.
The diagnosis at an early stage is necessary because early treatment can postpone the development and reduce complications.
Treatment: Management of Peripheral Neuropathy and its Effective Treatment.
Peripheral Neuropathy has no cure or treatment, but management of the kind of disorder can be applied to mitigate the symptoms and manage the pain and treat the causes.
-
Medications for Relief of Nerve Pain
- Mild pain can be addressed by the over-the-counter painkillers (acetaminophen and ibuprofen).
- Chronic nerve pain: Use of some prescription medications such as anticonvulsants (gabapentin, pregabalin) and antidepressants (amitriptyline and duloxetine).
- Topical treatments: Topical medications such as lidocaine patches, capsaicin creams, etc., for localized relief
-
Advantages of Physical Therapy
The individualized therapy programs are specific to target specific areas required to be improved on muscle strength, balance and flexibility. Physical therapists recommend using braces, orthotics, or mobility aids when necessary.
-
Methods of Nerve Stimulation
Low-voltage electrical impulses are employed to minimize pain with Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS).
-
Treating the Cause
- Diabetes: Maintain blood sugar level normal.
- Autoimmune illnesses: Adequate immunosuppressive treatments.
- Vitamin deficiencies: Adequate supplementation
- Infections: Adequate antibiotics or antiviral therapy
-
Cutting-Edge Treatments
Stem cell treatment, nerve regeneration and neuromodulation devices are a new ray of hope for the plight of patients with end-stage neuropathy.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Strategies for Enhancing Quality of Life
Neuropathy treatment largely depends on the daily activities of patients.
Nutritional Modifications to Neuropathic Pain.
- Consume foods high in vitamin B12, folate, vitamin E and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Reduce the consumption of processed sugar and manage blood sugar.
- Drink lots of fluids; consume lots of fruits and vegetables, which are antioxidants.
Alternative Treatments
- Acupuncture: removes nerve pains and advances blood circulation.
- Massage therapy: Massage relaxes muscles and aids in the health improvement of the nerves.
- Mindfulness and meditation: chronic pain & anxiety reduction.
Exercises to Lessen Symptoms
- Walking, yoga, tai chi, and swimming: This is low-impact exercise that helps boost blood flow and body bending.
- Strength training: Gives better muscle control.
Care for Feet and Hands
- Check feet and hands every day for any cuts, wounds, or infections.
- Wear the right shoes and never walk on bare feet.






